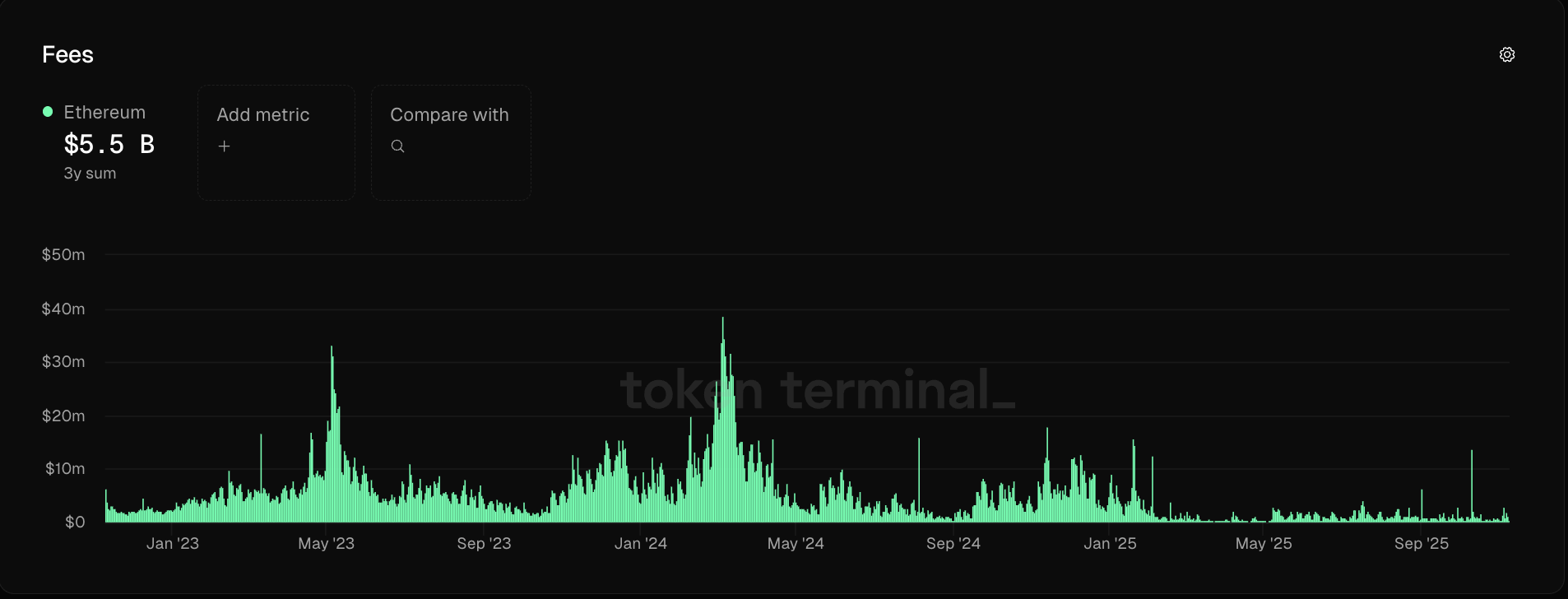
Recent developments in the Ethereum network highlight a significant shift in transaction costs, with gas fees plummeting to historic lows amid ongoing market uncertainties. As crypto markets experience a slowdown following October’s sharp market dip, transaction costs across Ethereum’s ecosystem have reached levels not seen in months, offering both opportunities and challenges for participants and stakeholders alike.
- Ethereum gas fees dropped to just 0.067 Gwei, making transactions extremely affordable.
- On-chain transaction costs currently average around $0.11, with NFT sales at $0.19.
- The decline follows a period of high fees during the October market crash, when fees peaked at 15.9 Gwei.
- Low fees have led to increased on-chain activity, but critics warn they threaten the sustainability of Ethereum’s fee model.
- Ethereum’s revenue from transaction fees has declined by 99% since the 2024 upgrade, raising concerns about network security and incentivization.
Gas fees on Ethereum’s layer-1 blockchain have fallen dramatically to their lowest levels in recent times, reaching just 0.067 Gwei on Sunday amid a subdued crypto market environment. This decline follows one of the most volatile periods in crypto history, marked by a market crash in October that pushed network transaction fees to 15.9 Gwei on October 10. Since then, fees have stabilized, remaining well below 1 Gwei throughout October and November, and currently averaging around $0.11 per transaction, according to Etherscan.
Traders are seizing the opportunity of low transaction costs to execute on-chain activities, yet industry experts warn that such-low fees could undermine the network’s long-term security and economic model.
Back in 2021, transaction fees during periods of network congestion could surpass $150, highlighting the dramatic reduction in costs since then. The March 2024 Ethereum Dencun upgrade, designed to lower fees for layer-2 scaling solutions, was a pivotal factor in this decline, leading to a 99% drop in the network’s fee-based revenue, as reported by industry analysts.
> Critics warn that the persistently low transaction fees could threaten the security of the Ethereum network by reducing blockchain validators’ incentives to process transactions and maintain network integrity. Low fees and revenues might also indicate that users are increasingly migrating away from the base layer, favoring layer-2 solutions for scalability.
Ethereum’s approach to scaling relies heavily on an ecosystem of layer-2 networks, which—while alleviating congestion and reducing costs—also challenge the sustainability of the main chain’s revenue model. According to research from Binance, this layered strategy may act as a double-edged sword, within the broader context of blockchain competitiveness and security concerns.
As the ecosystem evolves, balancing low transaction costs with network security remains a key challenge for Ethereum and the wider blockchain industry.
For now, the low fee environment provides an attractive window for users to execute faster and cheaper transactions, but its long-term implications continue to be a topic of debate among industry leaders and analysts alike.







